Everything You Need to Know About UID and MIL-STD-130
If you have never been contracted to handle government inventory or assets, you may not be aware of what UID Labels are or the importance of subscribing to MIL-STD-130 guidelines. These two systems play a critical role in the management of public assets as laid down by the Department of Defense. What is UID? A…
Everything You Need to Know About UID and MIL-STD-130
Everything You Need to Know About UID and MIL-STD-130
If you have never been contracted to handle government inventory or assets, you may not be aware of what UID Labels are or the importance of subscribing to MIL-STD-130 guidelines. These two systems play a critical role in the management of public assets as laid down by the Department of Defense.
What is UID?
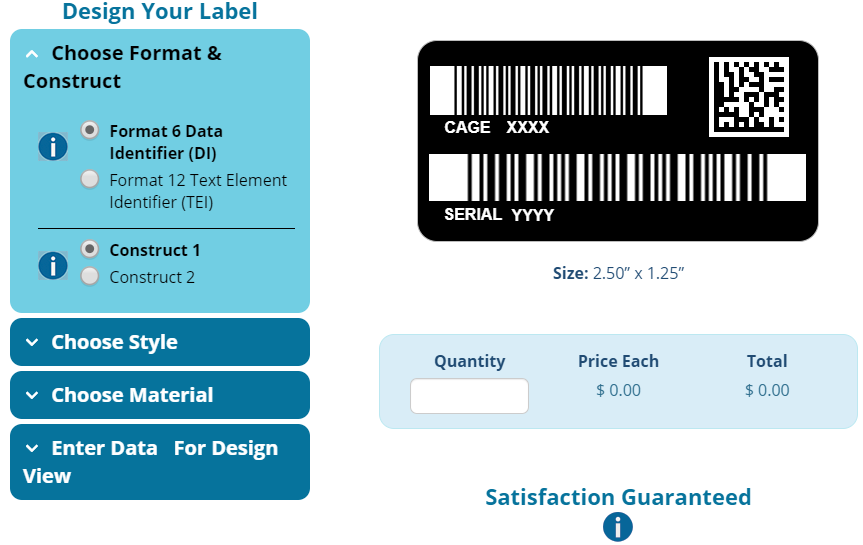
A UID system is a system put in place by the Department of Defense to ensure the ease of tracing government assets. The idea behind its creation is to design a unique identification number or code for each individual asset different from another. Furthermore, the difference in coding is to ensure that there are no duplicates of the same numbers. As long as the stipulated procedures are adhered to, accuracy and information reliability is sustained. The Department of Defense uses UID Labels to track the value of an asset, its location, quantity, and its current state. By so doing, the Department is able to monitor their usage and maintain them when necessary.
What is the difference between UID and IUID?
You may have come across assets with both inscriptions in the past and this may have caused you some form of confusion. You are however not alone as many people have had issues distinguishing between a UID Label and an IUID Label. The UID term is commonly used in referring to marking labels or asset tags and it has different names such as UID Code, UID Tag, or UID Label. However, the modern trend we observe today is that the term IUID is used to convey the specific identification of an asset.
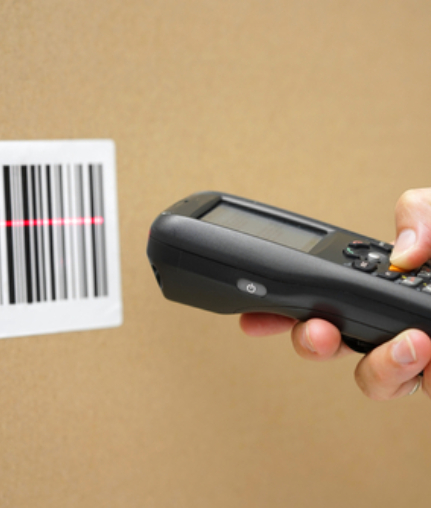
IUID labels use a special 2D barcode which can be scanned. The UII is the asset detail embedded in the barcode. When you scan this code, the information it contains can be tracked with special software. When analyzing UID, there are certain acronyms whose meanings hold vital importance. They are
UID– Unique Identification
IUID– Item Unique Identification
UII– Unique Item Identifier
Why is a UID Label so important?
If you are a current or prospective contractor, using UID Labels on assets is mandatory and not an optional choice. UID labeling is mandatory as per the DOD’s MIL-STD-130 guidelines for all government assets. It will interest you to know that even contractors demand UID on their assets as well. So, therefore, if you have a contract from the government to produce equipment for the military, you need to ensure that each individual equipment is labeled correctly using MIL-STD-130 specifications. For clarity’s sake, let us throw more light on MIL-STD-130 Basics.
MIL-STD-130 and the relationship with UID
When it comes to subscribing to the tenets of MIL-STD-130, there are a few complex marking requirements involved in the process. Under this guideline, the government of the US calls on all contractors handling military asset contracts to place special markings on the equipment that they produce. In accordance with these guidelines, the special UID Label should appear on all government purchased physical equipment. If you are a contractor and you want to be UID complaint, you will need to use UID Labels or marks on the asset that will last for as long as it’s lifecycle.
Best practices of MIL-STD-130
UID Labels are meant to withstand extreme weather conditions wherever they are deployed and these labels are expected to last a lifetime. As a contractor, it is advisable that you only pick a company that produces UID Labels using industry-standard best practices and complying with the DOD guidelines. A UID provider who understands the standards is in the best possible position to create labels that will not violate MIL-STD-130 rules. Very good providers ensure that
- Assets are marked properly
- Codes aid data management
- UID Labels are properly installed
- Registered items are MIL-STD-130 compliant
Benefits of installing quality UID Labels
Property accountability: UID Labels ensure that all assets are properly accounted for. Assets that are still in use can easily be differentiated from the ones that have been put out of commission.
Maintenance Management: Handling a few assets may not be a tough task, but when these assets or equipment number several hundred or thousands, it becomes a challenge to identify those in need of maintenance. With UID Labels, you can keep track of which individual asset has been maintained and at what time. This will help you regulate maintenance schedules for all of them.
Reduction in Operational Cost: Tracking assets in real-time costs a lot of resources. When tracking is done haphazardly, the cost of operation is more expensive. Proper UID markings can help decision-makers regulate the use of each asset so as to ensure that only the required assets are put to use at every specific point in time. This reduces the cost of deploying more assets than required.
Logistic Support: Perhaps the greatest benefit of using UID Labels is the Logistical support it provides users.
Warranty Management: Knowing when the warranty on each asset expires is part of an effective asset management strategy that the Department of Defense takes seriously. UID Labels can be used to ascertain the warranty placed on assets.
Report Accuracy: UID can be helpful when compiling a report on assets because every asset in each category can be tracked and their current state evaluated.
Avoid Rejections: Most importantly, if you are contractor, engraving the assets you supply to the DOD with quality UID’s will help you avoid rejections, which will cost you more resources to correct. The Department of Defense only accepts assets that meet standard MIL-STD-130 guidelines.
In conclusion, UID labels play an all-important role in asset management for the Department of Defense. These labels ensure sound asset management and accountability. They also aid efficiency and maintenance. If you are a DOD contractor, make sure that all the assets you deliver are engraved with standard UID Labels and you will have nothing to worry about.